Steam Access
Accessibility Widget for the Steam · Desktop Client Added Feature
A platform-wide accessibility hub designed to improve discoverability, customization, and inclusive gaming experiences on Steam.
🛠️ ROLE
Sole UX Researcher & UX Designer
📅 TIMELINE
65 Hours
🗂️PROJECT TYPE
Conceptual · Designlab UX Academy Capstone
💻 PLATFORM
Desktop (Steam Client & Web)
🛠️ TOOLS
Figma, Adobe Creative Cloud
🌟 SKILLS
User research, affinity mapping, personas, task flows, wireframing, prototyping, usability testing, accessibility design
PROJECT OVERVIEW
The Problem
Steam is one of the largest PC gaming platforms in the world, yet accessibility support is largely fragmented and inconsistent. Most accessibility options exist at the individual game level, making them difficult to find, compare, or trust before purchase. Steam also lacks platform-wide tools such as scalable text, color vision filters, screen reader support, and clear controller compatibility labeling.
As a result, players with disabilities, and those experiencing temporary or situational impairments, often rely on trial-and-error, external forums, or third-party tools to determine whether a game is playable.
The Opportunity / Solution
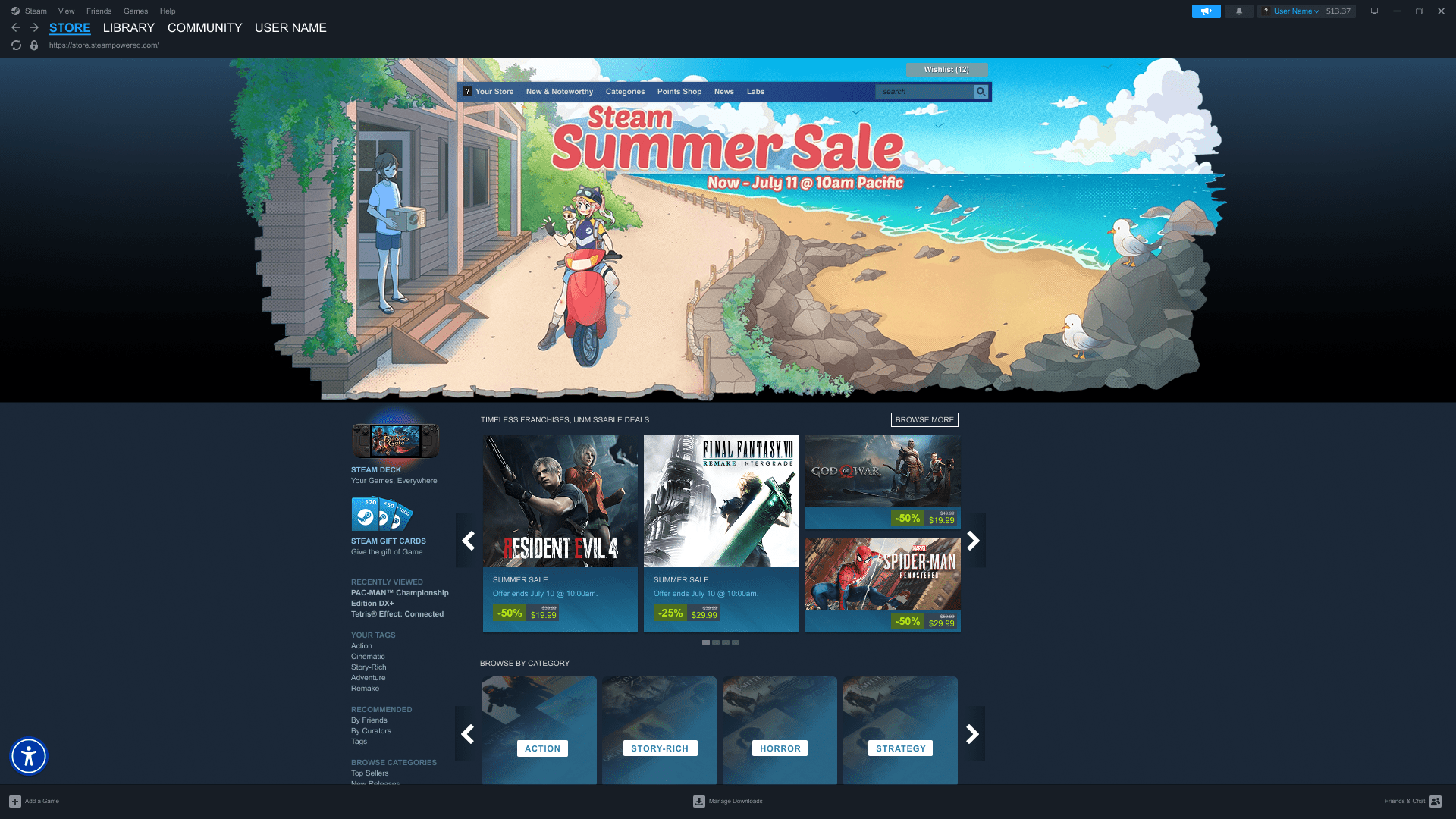
Steam Access introduces a centralized Accessibility Widget embedded directly into the Steam desktop experience. The widget enables users to:
Discover accessibility features before purchasing games
Customize visual and input settings at the platform level
Save and reuse accessibility profiles
Rely on community-driven accessibility feedback
By treating accessibility as a core platform feature rather than an afterthought, Steam Access reduces friction while preserving familiar Steam workflows.
Outcome (Conceptual)
This project demonstrates how accessibility can be thoughtfully integrated into an existing, complex product ecosystem—improving usability for players with disabilities, while also benefiting casual users, players with temporary impairments, and those seeking comfort-focused features.
RESEARCH
Research Goals
Understand accessibility challenges users face when navigating Steam
Identify gaps in discoverability, customization, and consistency
Learn how players evaluate accessibility before purchasing games
Secondary Research – Competitive Analysis
I reviewed accessibility standards and analyzed how major gaming platforms support accessibility at the system level. This comparison focused on platform-wide features, discoverability, and consistency, rather than individual game settings.
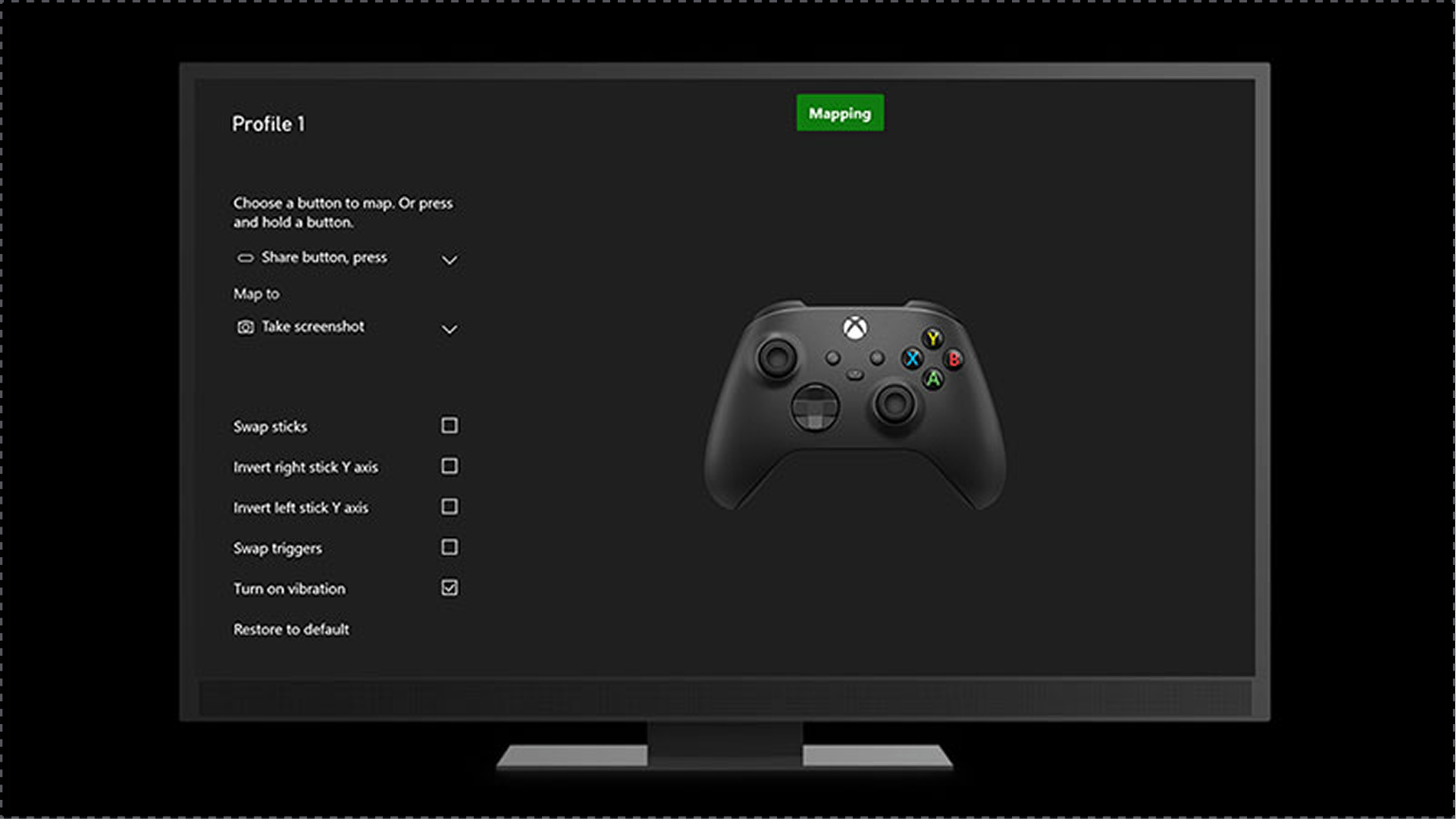
Competitor 1: Xbox (Microsoft)
✅ System-wide accessibility settings across the platform
✅ Strong adaptive controller support and input remapping
✅ Clear accessibility tags in the game store
❌ Accessibility features still vary by game
❌ Setup can feel complex for new users
❌ Adaptive hardware can be costly
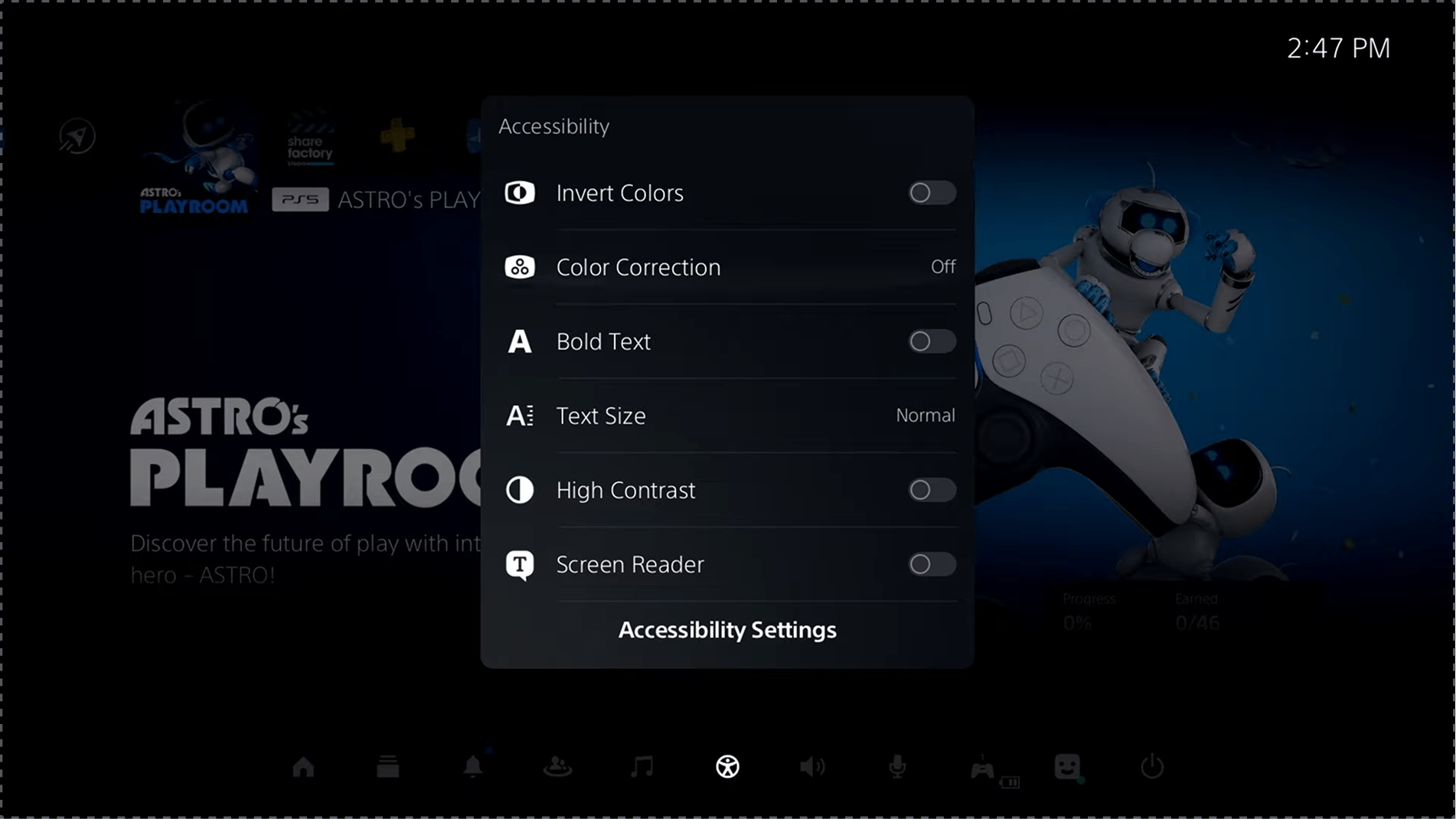
Competitor 2: PlayStation (Sony)
✅ Comprehensive system-level visual and input accessibility settings
✅ Dedicated accessibility controller for physical needs
✅ Built-in text-to-speech and display customization
❌ Accessibility tags are limited in the game store
❌ Features are not consistently implemented across games
❌ Proprietary hardware limits flexibility
Competitor 3: Epic Games Store
✅ Popular titles with some in-game accessibility options
❌ No platform-wide accessibility settings
❌ Lacks accessibility filters or tags in the store
❌ Heavy reliance on individual games for accessibility support
This analysis highlighted a clear gap between console ecosystems, which offer centralized accessibility tools, and PC-first platforms, where accessibility is often fragmented or game-dependent. These gaps reinforced the need for a centralized, platform-level accessibility solution within Steam.
Primary Research – User Interviews & Research Synthesis
I conducted five in-depth interviews with gamers aged 26–43, including players with visual impairments, motor limitations, temporary injuries, and accessibility advocates. Using affinity mapping, I identified three key clusters that directly informed the Tritanopia task flow and visual accessibility design.
Discoverability
→ Design impact: Led to a centralized Accessibility Widget accessible from the Steam homepage
Color & Contrast
→ Design impact: Prioritized a Tritanopia-focused color vision flow with before/after previews to improve contrast in pricing and sale indicators
Physical Strain & Visual Fatigue
→ Design impact: Informed simplified visual hierarchy and improved contrast clarity to reduce visual fatigue during browsing.
DEFINE
Personas
Three personas were drafted to represent a range of accessibility needs across Steam. While each persona informed the broader problem space, the vision-supportive gamer most directly guided design decisions—shaping the focus on color contrast, visual clarity, and platform-level accessibility settings.
Problem Framing
Research findings were translated into focused How Might We questions, including:
Visual Accessibility
How might we help gamers with low vision browse Steam independently?
How might we support users who need high contrast or larger text without overwhelming the interface?Inclusive Defaults & Onboarding
How might we allow users to configure and save accessibility settings before gameplay?
Key Task Flows
Two task flows were initially explored to support both visual and physical accessibility needs. Based on research findings and project scope, the flow for adjusting color and contrast for Tritanopia was selected and adapted as the primary design focus, as it best demonstrated how a platform-level accessibility feature could improve discoverability, clarity, and user confidence within Steam’s existing interface.
DESIGN
Mid-Fidelity Exploration
Mid-fidelity wireframes focused on information hierarchy, discoverability, and integration within Steam’s existing desktop interface. Early exploration tested where an Accessibility Widget could live without disrupting established navigation patterns.
Usability Testing & High-Fidelity Design
Seven mid-fidelity screens were tested with the original five research participants. Testing evaluated:
Discoverability of the Accessibility Widget
Clarity of color vision deficiency presets
Confidence when previewing and applying visual changes
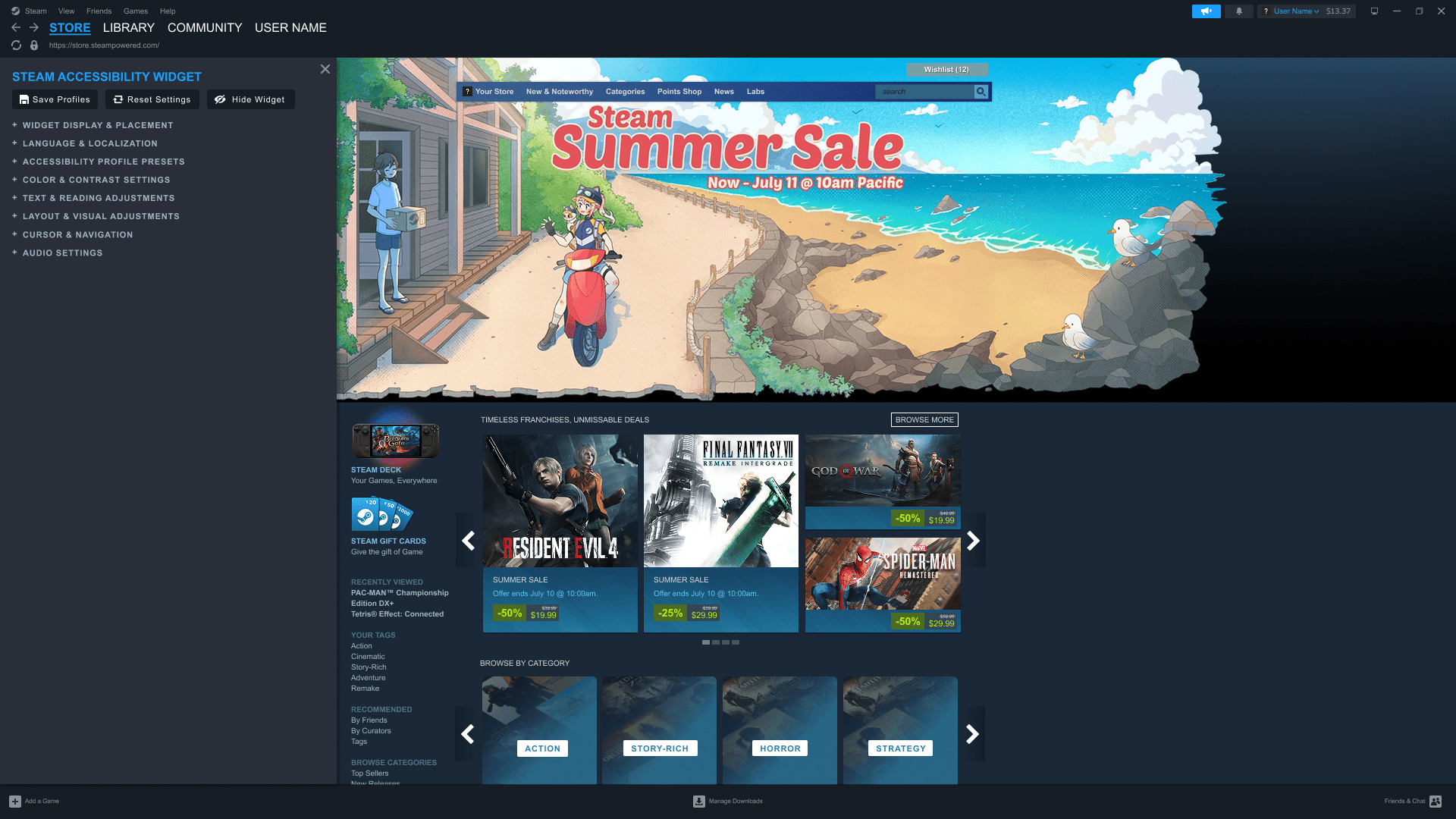

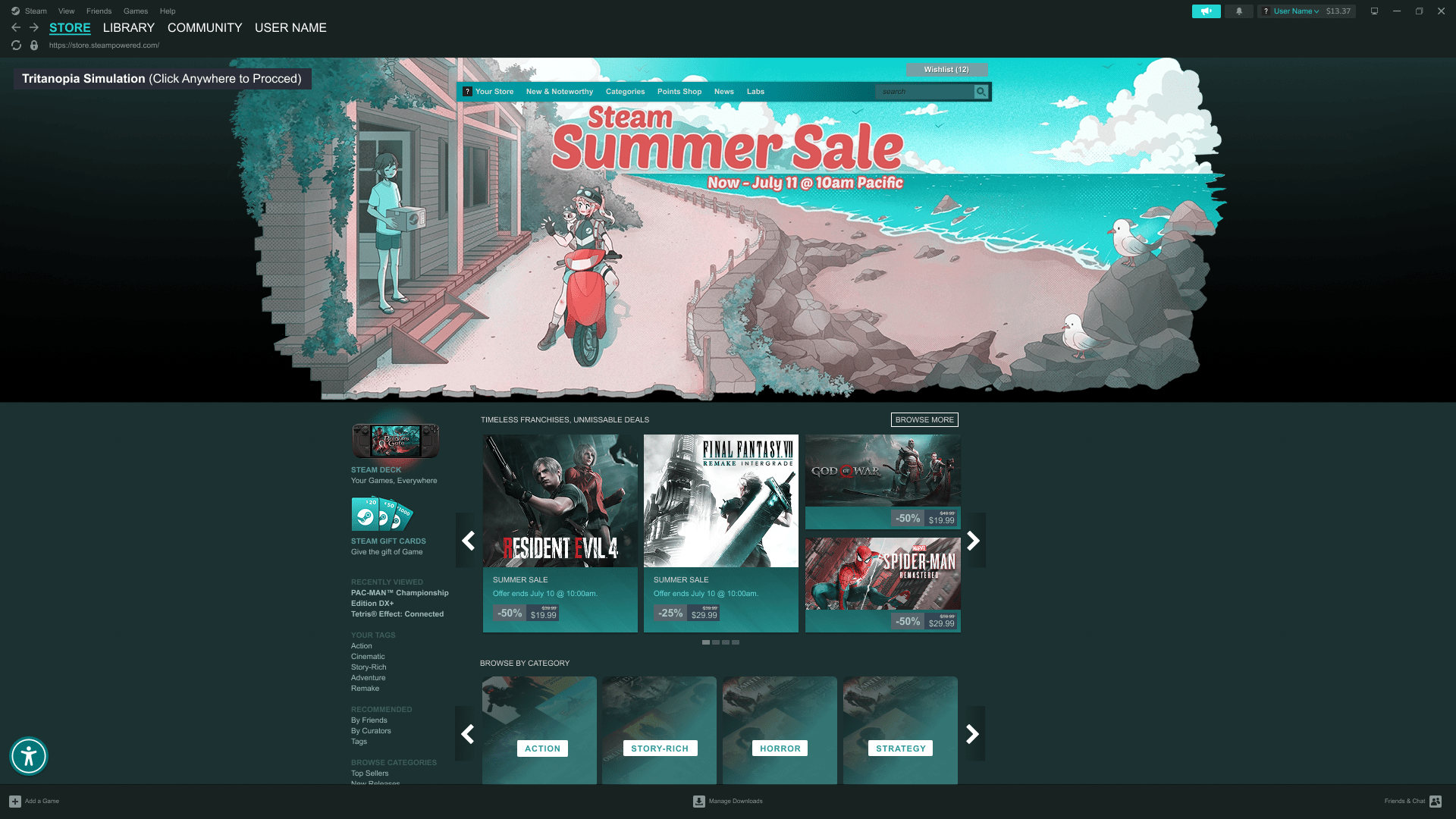
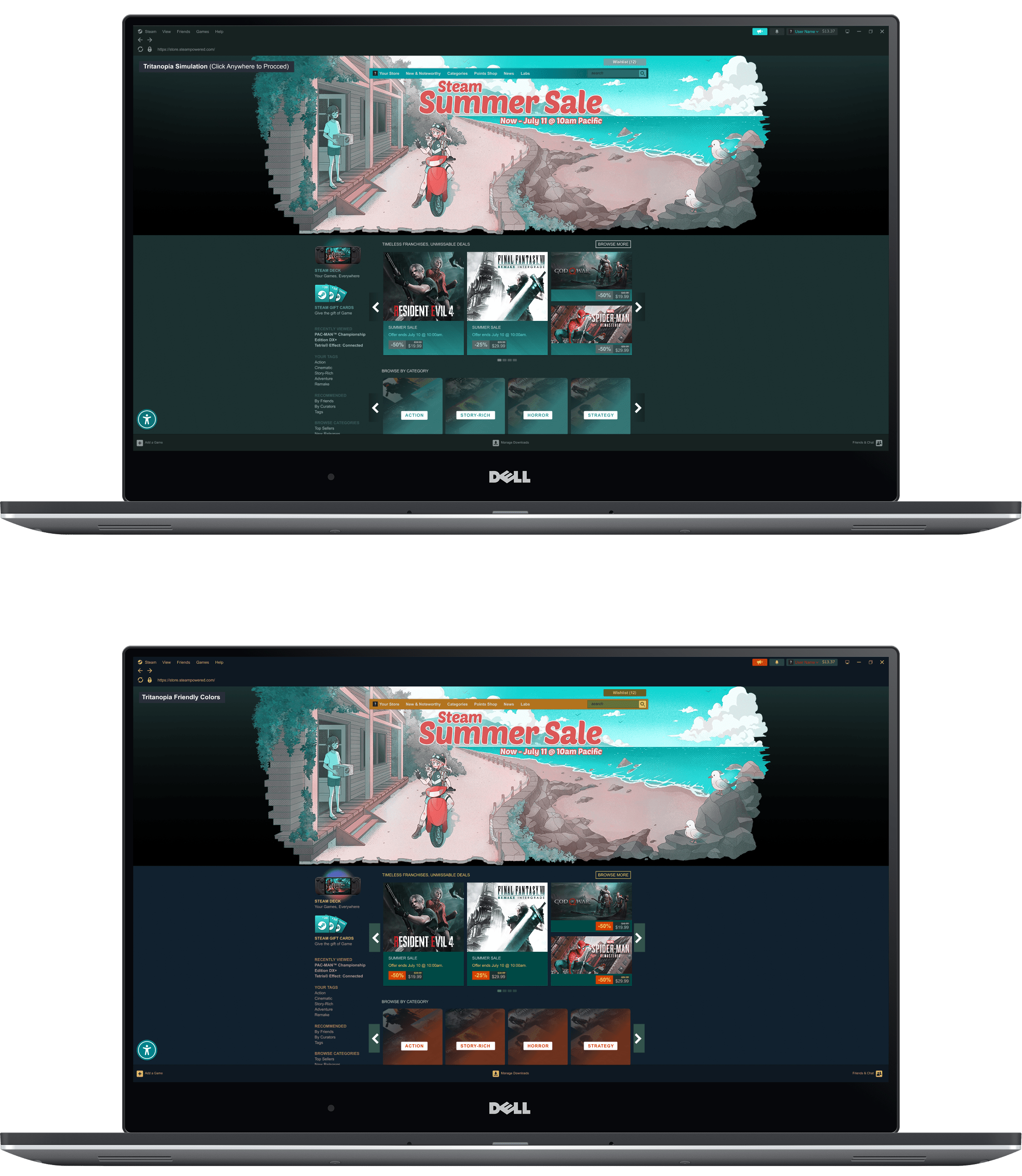
Steam Access integrates platform-wide accessibility controls directly into the Steam desktop experience, allowing users to discover and customize visual settings without leaving the homepage.
Preview of the Steam interface as experienced by users with Tritanopia, followed by the adjusted color configuration designed to improve contrast, clarity, and readability
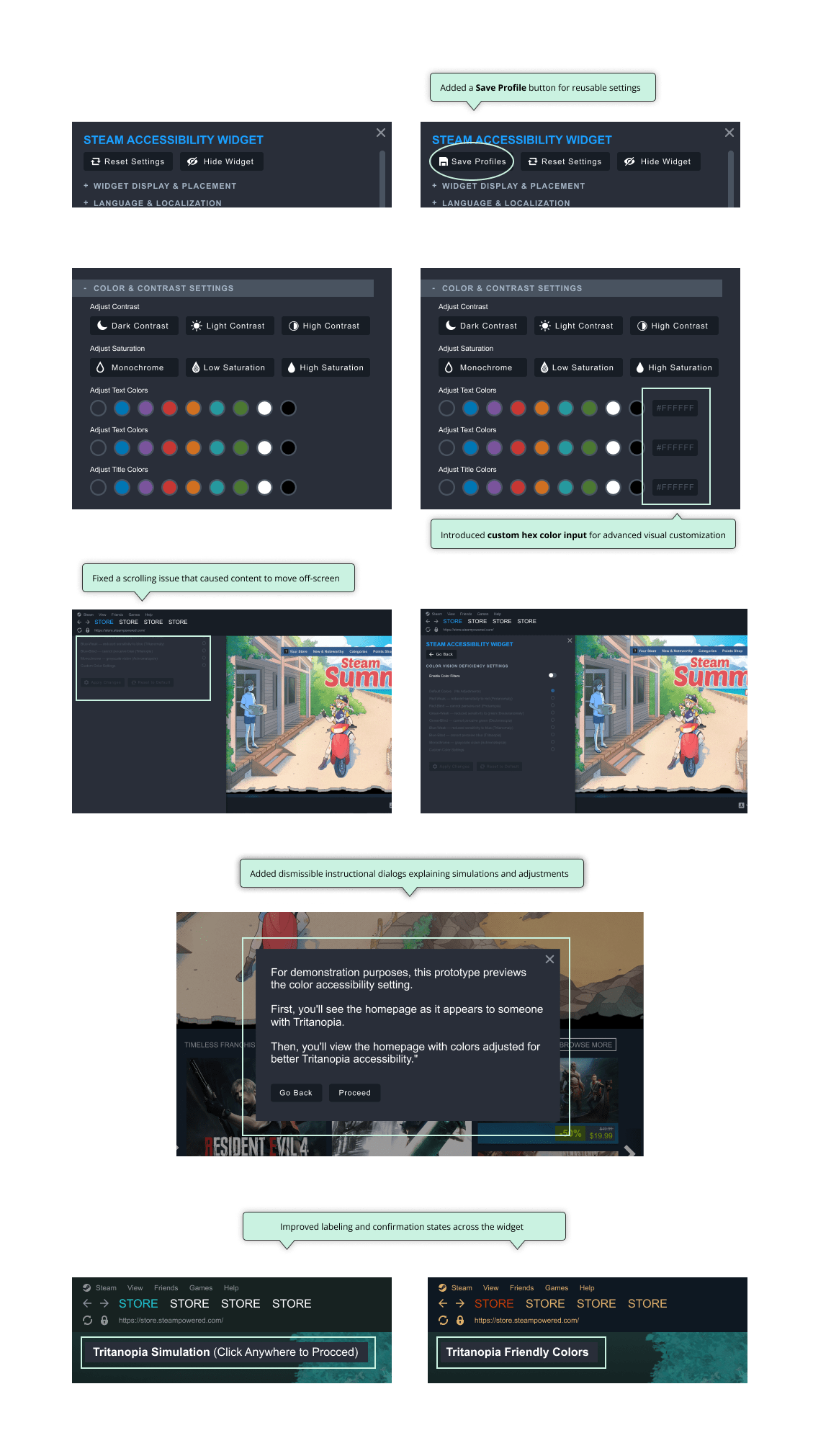
Participants responded positively to the centralized menu, and usability testing informed refinements such as saveable accessibility profiles, custom hex color inputs, and clearer prompts and labels to improve clarity and user control.
Iterations
Based on usability findings, I iterated to improve clarity and control:
FINAL SOLUTION
Key Features
Platform-wide Accessibility Menu
Accessibility tag filters for game discovery
Color vision deficiency presets with live previews
Saveable accessibility profiles
Community-driven accessibility reviews
Experience Overview
Users can preview how the Steam interface appears with specific visual impairments, apply accessible color adjustments, save settings, and revert changes with confidence. The experience prioritizes clarity, control, and trust without overwhelming users.
IMPACT & REFLECTION
Outcomes
All participants successfully completed core tasks after minor orientation
Average satisfaction rating of 4.1 / 5
Increased confidence once accessibility features were located and applied
Strong validation for centralized, platform-level accessibility
Key Learnings
This project reinforced that accessibility must be designed at the system level—not added game by game. It also highlighted the importance of balancing flexibility with simplicity to avoid cognitive overload in accessibility-focused interfaces.
Future Opportunities
Expanded presets for motor and cognitive accessibility
Voice navigation for hands-free interaction
Accessibility-focused game curation and recommendations
WHY THIS MATTERS
Steam Access illustrates how inclusive design can scale within an established platform. By embedding accessibility directly into the core desktop experience, Steam has the opportunity to support a broader range of players, build trust, and set a higher standard for accessibility in PC gaming.